The Many Qualities of Heat Shrink

With its many manufacturers, materials, and uses, heat shrink specifications may become a little overwhelming to the uninformed buyer. But across the board, the tubing is a versatile, flexible, adhesive, and organizational tool for just about any of its applications.
Looking to snag some for your next project? Read on to learn about all the incredible qualities of heat shrink tubing before you jump in.
What is heat shrink?
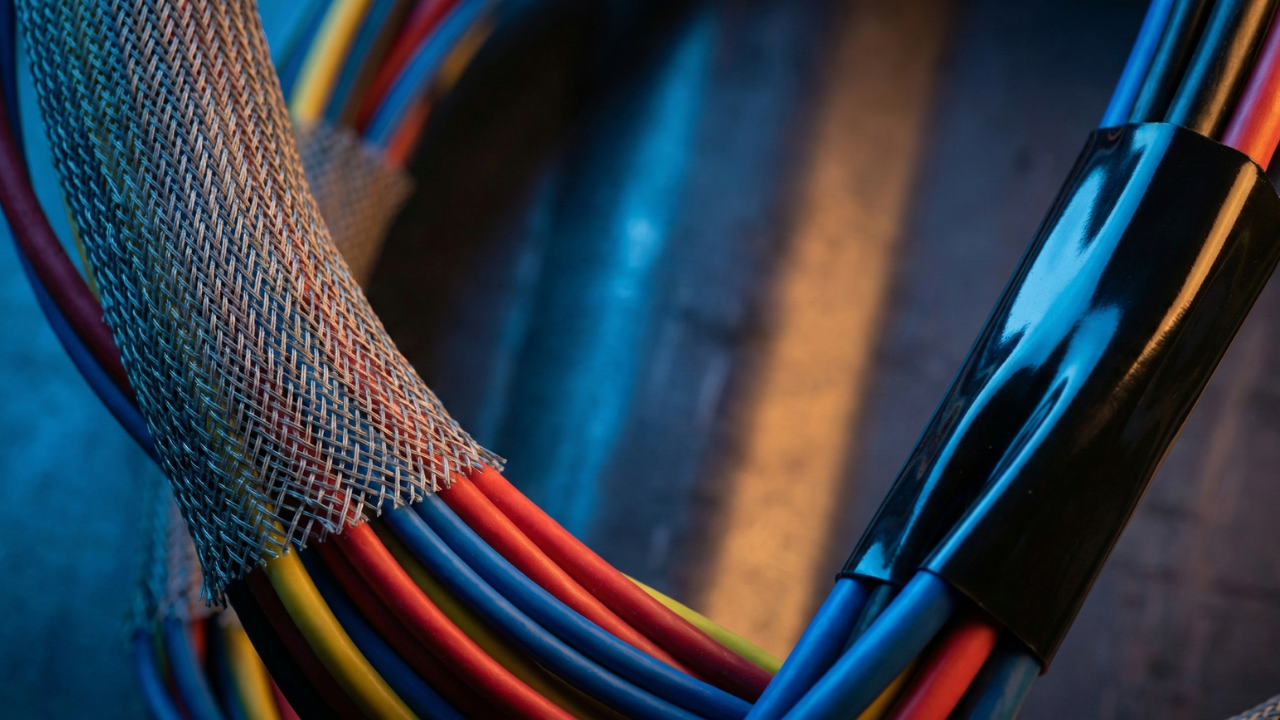
Heat shrink tubing, often referred to as just heat shrink, is a piece of tubular polymer that is available in many different kinds of materials to serve a variety of purposes. As its name suggests, the tube shrinks radially when exposed to heat, making it particularly useful for electrical insulation to wires, connections, joints, terminals, and splices. The material is also a handy solution when bundling loose items, like wires, or even just applying a protective covering.
Heat shrink is produced using a two-step process that begins with standard extrusion. The material of which the tubing is made is carefully selected depending on the purpose for which the tube will be utilized and what kind of environment it will be in. The chosen base material is then mixed with other additives, such as colorants and UV stabilizers.
Secondly, heat and force are used in order to expand the diameter of the tubing. After cooling from this process to a comfortable room temperature, the tubing is then able to be exposed to a heat source again to shrink to its original size. Of course, if used around another material, such as wiring in need of insulation, the heat shrink tubing will only reduce enough to fit firmly around it.
Heat shrink is versatile
Whether insulating, bundling, or covering, there is a heat shrink tubing material suitable for just about any occasion. Most commonly made from polyolefin, standard heat shrink has maximum continuous-use temperatures that range from -55 to 135 °C, shrinking 2:1 diametrically at 143°C. However, some high-grade polyolefin heat shrink has a 3:1 ratio. This standard is often used by the military, aerospace, and railway industries but is also available for commercial purchase and use.
Of course, the list of materials and best applications spans well beyond that of polyolefin. Elastomeric tubes provide excellent resistance to abrasion, even in harsh environmental conditions. Fluoropolymer (PTFE) heat shrink tubes have wide operating temperature ranges and high resistance to chemicals and punctures. Fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP) is a lower-cost alternative to PTFE and an incredibly versatile electrical insulator.
Better yet, many more special materials exist as heat shrink, even providing resistance to diesel and aviation fuels, increased abrasion resistance, and other uses.
Is heat shrink conductive?
Though heavily associated with insulating electrical components, heat shrink tubing can also come with conductive lining. Particularly used on joints that are not soldered, or joined together by melting and adhering filler metals, some are constructed to act as wire connectors, thanks to its thick inner coating that condones electrical continuity.
Is heat shrink adhesive?
Yet another fantastic quality of heat shrink is its levels of adhesion. Whether built with inner thermoplastic materials to provide airtight seals or reliant on friction between closely conforming materials, heat shrink can stay firmly put. Additionally, non-adhesive shrink tubing may also be fused to its underlying material by heating it near its melting point.
Is heat shrink flexible?
Because of its two-step manufacturing process, pre-stretched heat shrink tubing is an incredibly flexible material. Some materials, like elastomeric tubes, are engineered to maintain high flexibility even at low temperatures.
Whether used to bind a handful of wires or travel the winding length of one as an insulator, heat shrink’s flexibility is yet another characteristic that allows it to perform with versatility.
Organizational
Heat shrink tubing is often manufactured in a wide range of colors (including transparent options) for color-coding specific wires. However, since colored materials typically have a lower resistance to ultraviolet light, black is the standard for outdoor applications.
Even inexpensive PVC tubing can take a variety of colors with ease, while also being available in opaque and transparent options. Buyers typically opt for PVC when in search of brighter and more vibrant colors.
Moreover, heat shrink tubing and tape can also be produced with customizable labels printed onto the material, to help specifically identify all your wires and cables.
If applied to an abundance of surfaces, color, transparency and labels in heat shrink can provide needed distinction.
No matter the use, heat shrink tubing is an essential component to securing, insulating, and organizing hardware in a variety of contexts. With a little product research, finding the best kind of material for your next project at or under budget is a lot easier than you may think.
Want to know more about heat shrink?
Hopefully, this guide has helped you understand the amazing things heat shrink tubing provides for your applications. Set up an account or log in to put in an order.
If you have additional questions, visit our learning center or FAQs. Or you can contact us here with questions or to receive a sample.